Research & Innovation
Multisite research, including research at UAB, shows that oral semaglutide is nearly as effective as the widely used injectable version for treating obesity, delivering about 13.7 percent average weight loss over 64 weeks.
In partnership with the Housing Authority of the Birmingham District, the City of Birmingham and community partners, UAB will assess the effectiveness of public housing renovations and environmental refinements on community health.
Sedative choice could improve patient outcomes in patients who have been intubated.
A new study reveals how a bacterial gene and FIVAR-equipped proteins allow pneumonia bacteria to invade heart cells, causing severe cardiac damage.
The award, totaling over $2 million through 2030, will support Overstreet’s investigation aimed at uncovering the factors that determine patients’ experiences of acute and chronic pain during their healing journeys after surgery.
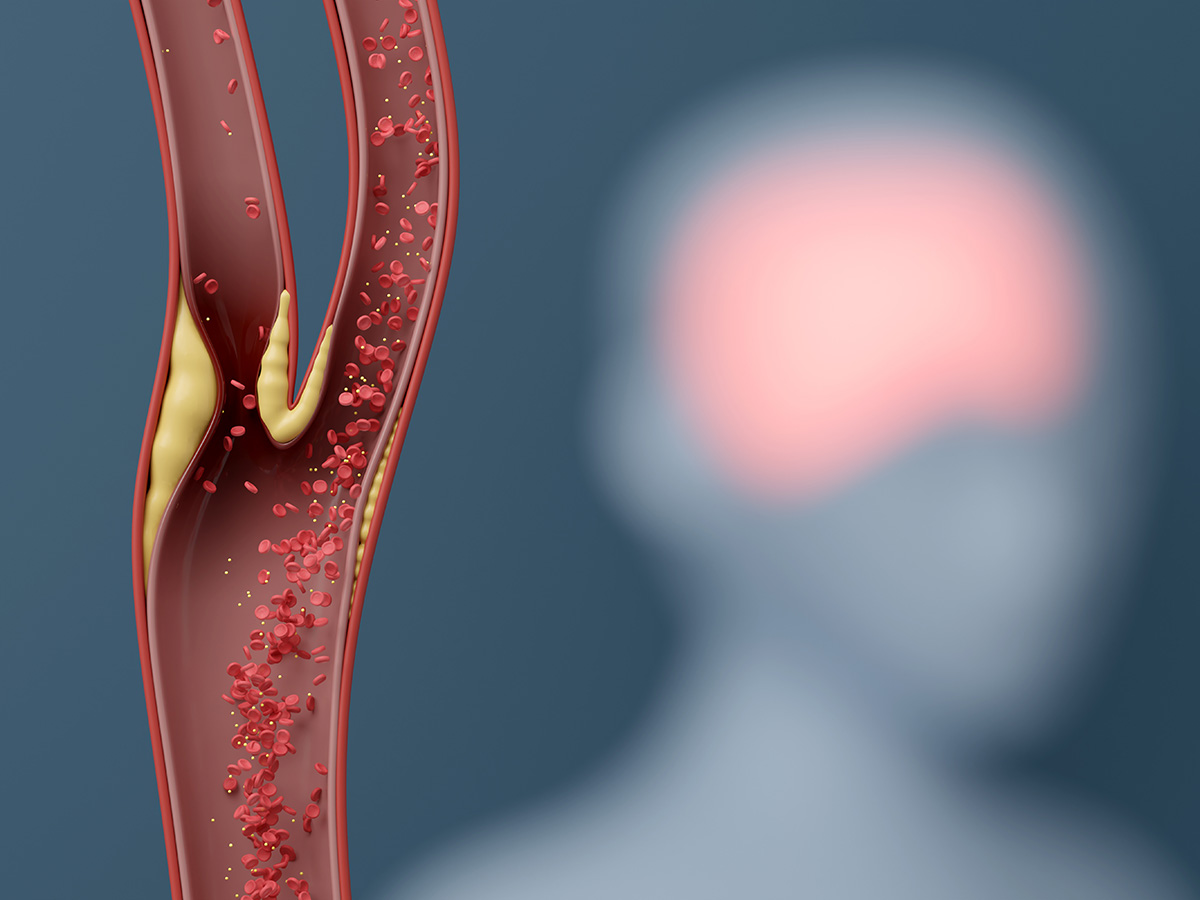
New research co-led by the UAB School of Public Health could reshape treatment guidelines for asymptomatic carotid stenosis, a condition caused by a buildup of plaque in arteries that carry blood to the brain.
One UAB researcher has received two grants from the NIH to study devices for diabetes and cardiopulmonary function of infants.
A UAB assistant professor is leading two studies to determine whether atherosclerosis can be prevented before it leads to diseases like heart disease.
UAB researchers have begun testing on a bacteria-derived protein, and early studies show it could lower cholesterol and improve metabolism.
UAB School of Optometry professor is joining a national network study to research myopia prevention in children.
If the GOALPOST Trial is successful, national guidelines for the treatment of non-severe HDP could change, revolutionizing the way patients are treated.
UAB researchers will develop three-dimensional models of the human brain that will be launched to the International Space Station, where they will remain for 30 days.
A new clinical trial is investigating how different amounts of breast milk affect the growth and health of premature babies, aiming to find the best feeding strategy for their early development.
Until now, treatments have only managed symptoms, rather than altering the disease’s course.
A UAB assistant professor in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Neurobiology has received a $3.5 million grant to study how hormones influence the female brain’s response to trauma.
UAB faculty members and students identified systemic barriers and proposed actionable strategies for supporting formerly incarcerated individuals’ reentry into the workforce.
UAB professor receives a $3.7 million grant to study how the genetic risk of high blood pressure affects the behavior of young and middle-aged adults.
UAB’s chief of MRI discusses how white matter hyperintensities may not be an accurate indicator for mild traumatic brain injury.
UAB researchers are using vagus nerve stimulation to improve physical therapy outcomes for Parkinson’s patients and advance neurologic rehabilitation.
Inspired by a police press conference, Computer Science Professor Yuliang Zheng, Ph.D., developed a way to prove that digital files are authentic while obscuring secret information, which is now an International Standard in cybersecurity.
A study published in Nature Microbiology shows that SARS-CoV-2 triggers foam cell formation in lungs, contributing to long-COVID lung damage, which can be mitigated by early antiviral treatment with molnupiravir.
UAB’s Mieke Thomeer McBride, Ph.D., one of the co-directors of the center, is carrying out the NIA’s mission to position the United States as the gold standard in aging research.
The study will investigate whether ctVNS administered using a hand-held cognitive performance device can measurably improve focus, mood and athletic performance among student-athletes.
These new findings help simplify the treatment for patients with syphilis.
RP59, a genetic cause of blindness, interrupts nerve signal transmissions from photoreceptor cells to the retinal bipolar cells.
To continuously produce neurons in the nose, a unique toggle switch generates transient cellular neighborhoods that integrate signaling at multiple scales — from single cells to groups of cells, to entire organs.
Nathan Shock Centers across the nation are funded by the National Institute on Aging to provide leadership in the pursuit of basic research into the biology of aging.
UAB researchers say this study shows passive antibody therapy can dramatically reduce Zika virus infection in critical tissues that could potentially lead to decreased transmission of virus through sex and from pregnant mothers to their babies.
This is the first detailed study of how and where ORC subunits regulate epigenetics and gene expression in human cells.
Aphantasia is the inability to create mental images, and many individuals with the condition remain unaware until adulthood.